Service Details
Breast cancer
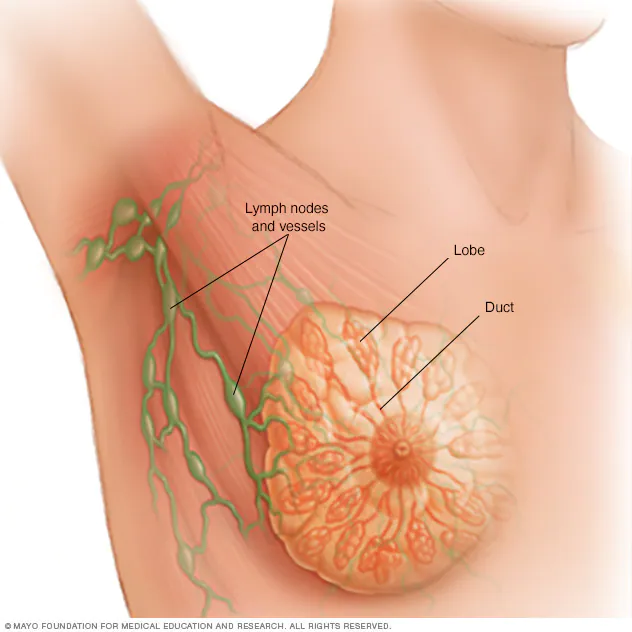
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the cells of the breast. It is one of the most common cancers affecting women, but it can also occur in men, although it is much rarer. Breast cancer usually starts in the milk ducts or the glands that produce milk (lobules) in the breast.
Risk factors for developing breast cancer include age (the risk increases with age), a family history of breast cancer, certain gene mutations (such as BRCA1 and BRCA2), personal history of breast cancer or certain benign breast conditions, early menstruation (before age 12) or late menopause (after age 55), never giving birth or having the first child after age 30, hormone replacement therapy, obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Symptoms of breast cancer may include a lump or thickening in the breast or underarm area, changes in breast size or shape, changes in the nipple (such as inversion or discharge), redness or scaling of the skin on the breast or nipple, and breast pain. However, it's important to note that not all lumps or changes in the breast are cancerous, and many breast changes are normal or benign.
To diagnose breast cancer, various tests may be performed, including mammography (X-ray of the breast), ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and biopsy (removal of a sample of tissue for examination). Once diagnosed, the stage of the cancer is determined, which helps guide treatment decisions.
Treatment options for breast cancer depend on the stage and characteristics of the cancer, as well as individual factors. Common treatment modalities include surgery (such as lumpectomy or mastectomy), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and hormone therapy. The goal of treatment is to remove or destroy the cancer cells and prevent their spread to other parts of the body.
Regular breast self-exams, clinical breast exams by a healthcare provider, and mammograms are important for early detection of breast cancer. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and survival.
It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized information, guidance, and advice regarding breast cancer prevention, screening, and treatment.
