Service Details
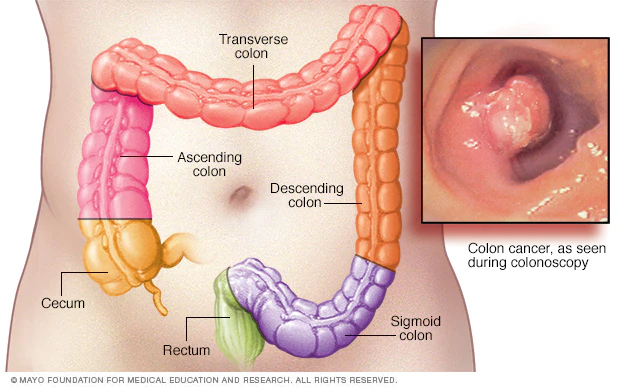
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer, also known as bowel cancer or colon cancer, is a type of cancer that originates in the colon or rectum. It usually starts as a polyp, which is a small growth on the inner lining of the colon or rectum. Over time, these polyps can become cancerous and invade nearby tissues and organs.
Here are some key points about colorectal cancer:
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms of colorectal cancer include changes in bowel habits (such as diarrhea or constipation), blood in the stool, abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying. However, early-stage colorectal cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms, which is why screening is important.
-
Risk factors: Several factors can increase the risk of developing colorectal cancer. These include age (the risk increases with age), a personal or family history of colorectal cancer or polyps, a history of inflammatory bowel disease (such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis), a sedentary lifestyle, a diet high in processed meats and low in fiber, obesity, smoking, and heavy alcohol consumption.
-
Screening and diagnosis: Regular screening is crucial for the early detection of colorectal cancer, as it can often be treated more effectively when found at an early stage. Common screening methods include colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, fecal occult blood tests, and stool DNA tests. If abnormalities are found during screening or if symptoms are present, further diagnostic tests like biopsies, imaging scans, and blood tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
-
Treatment: The treatment options for colorectal cancer depend on the stage of the cancer, its location, and the overall health of the patient. Common treatment modalities include surgery to remove the tumor and nearby lymph nodes, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The treatment plan is usually determined by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
-
Prevention: While it may not be possible to prevent colorectal cancer entirely, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk. These include adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting the consumption of processed meats, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, moderating alcohol intake, and undergoing recommended screening tests.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice, especially regarding screening and prevention strategies, as they can take into account your specific risk factors and medical history.
